Understanding Interline Spacing: A Comprehensive Guide to Line Height
In the world of typography and design, interline spacing, often referred to as line height, plays a crucial role in readability and visual appeal. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of interline spacing, exploring its definition, importance, measurement, and best practices for various applications. Whether you’re a seasoned designer or a novice content creator, understanding interline spacing is essential for creating visually engaging and easily readable text.
What is Interline Spacing?
Interline spacing, or line height, refers to the vertical distance between the baselines of successive lines of text. The baseline is the imaginary line upon which most letters sit. Adjusting the interline spacing can significantly impact the overall look and feel of a document, website, or any other form of text-based communication. Too little space can make the text appear cramped and difficult to read, while too much space can make it feel disjointed and fragmented.
Why is Interline Spacing Important?
The importance of interline spacing extends beyond mere aesthetics. It directly affects readability, comprehension, and the overall user experience. Here’s a closer look at why it matters:
- Readability: Adequate interline spacing allows the reader’s eye to easily track from one line to the next, reducing eye strain and improving reading speed.
- Comprehension: When text is easy to read, readers are more likely to understand and retain the information presented. Inadequate interline spacing can lead to misinterpretation and frustration.
- Visual Appeal: The right interline spacing can enhance the visual appeal of a design, making it look more professional and polished. It contributes to the overall balance and harmony of the layout.
- Accessibility: Proper interline spacing is crucial for users with visual impairments or reading disabilities. It can significantly improve their ability to access and understand the content.
Measuring Interline Spacing
Interline spacing is typically measured in points (pt) or as a multiplier of the font size. In many design and word processing applications, you can specify the line height as a specific value (e.g., 14pt) or as a relative value (e.g., 1.5). The relative value is often the preferred method, as it automatically adjusts the interline spacing proportionally to the font size. For example, a line height of 1.5 means that the space between lines is 1.5 times the font size.
Common Units of Measurement:
- Points (pt): A traditional unit of measurement in typography, where 1 point is approximately 1/72 of an inch.
- Pixels (px): A unit of measurement commonly used in web design, representing a single dot on a screen.
- Ems (em): A relative unit of measurement, where 1 em is equal to the current font size.
- Percentages (%): Similar to ems, percentages are relative to the font size. 100% is equivalent to 1 em.
- Unitless (no unit specified): This often defaults to a multiplier of the font size, such as 1.5, which means 1.5 times the font size.
Best Practices for Interline Spacing
Choosing the right interline spacing depends on several factors, including the font size, font style, line length, and the overall design context. Here are some general guidelines to follow:
- General Body Text: For body text, a line height of 1.4 to 1.6 is generally recommended. This provides sufficient space for comfortable reading.
- Headings and Subheadings: Headings and subheadings often benefit from slightly tighter interline spacing (e.g., 1.2 to 1.4) to create a more compact and visually distinct appearance.
- Longer Line Lengths: When working with longer line lengths, increase the interline spacing to improve readability. The longer the line, the more space is needed for the eye to track comfortably.
- Shorter Line Lengths: For shorter line lengths, you can often use slightly tighter interline spacing without sacrificing readability.
- Font Style: Different fonts have different x-heights (the height of lowercase letters), which can affect the perceived interline spacing. Experiment with different values to find what works best for each font.
- Consider the Target Audience: When designing for users with visual impairments or reading disabilities, prioritize generous interline spacing to maximize accessibility.
Interline Spacing in Different Applications
The principles of interline spacing apply across various applications, from print design to web design and word processing. Here’s a brief overview of how interline spacing is handled in each:
Print Design:
In print design software like Adobe InDesign, interline spacing is typically controlled through the “Leading” setting. You can specify the leading value in points or as a percentage of the font size. Print design allows for precise control over all aspects of typography, including interline spacing.
Web Design:
In web design, interline spacing is controlled using the CSS `line-height` property. You can specify the line height in pixels, ems, percentages, or as a unitless value. Using relative units like ems or percentages is generally recommended for responsive design, as it allows the interline spacing to scale proportionally with the font size on different screen sizes.
Example CSS:
p {
line-height: 1.5;
}
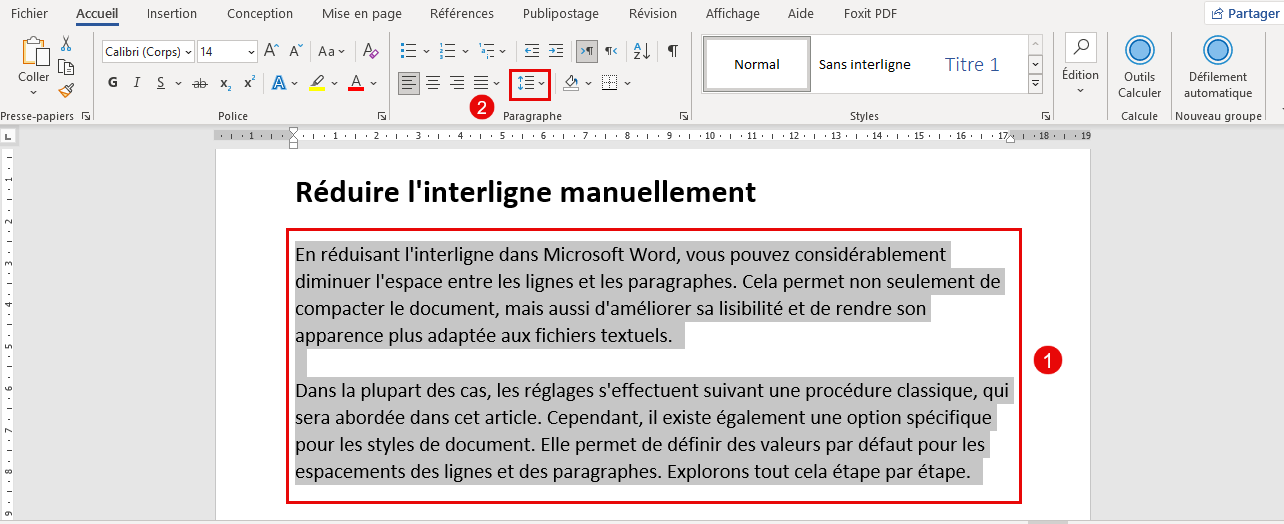
Word Processing:
In word processing software like Microsoft Word or Google Docs, interline spacing is typically controlled through the “Line Spacing” settings. You can choose from predefined options like single, 1.5, double, or specify a custom value. Word processing applications offer a user-friendly interface for adjusting interline spacing and other typographic settings.
Tools for Adjusting Interline Spacing
Numerous tools are available to help you adjust and optimize interline spacing in your designs and documents. Here are a few popular options:
- Adobe InDesign: A professional-grade layout and design software with advanced typography controls.
- Adobe Photoshop: While primarily a photo editing tool, Photoshop also offers basic typography features, including interline spacing adjustments.
- Microsoft Word: A widely used word processing application with line spacing options.
- Google Docs: A free, web-based word processor with basic line spacing controls.
- Online CSS Editors: Various online CSS editors allow you to experiment with `line-height` and other CSS properties in real-time.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While interline spacing may seem like a simple concept, there are several common mistakes that designers and content creators often make. Here are a few to avoid:
- Using Default Settings: Relying on default interline spacing settings can often result in suboptimal readability. Always take the time to adjust the settings to suit the specific font, line length, and design context.
- Inconsistent Spacing: Maintaining consistent interline spacing throughout a document or website is crucial for creating a professional and polished look. Avoid using different values for different sections of text unless there is a clear design rationale.
- Ignoring Line Length: Failing to consider line length when setting interline spacing can lead to readability issues. Remember to increase the line height for longer lines and decrease it for shorter lines.
- Overly Tight Spacing: Using interline spacing that is too tight can make the text appear cramped and difficult to read. Always prioritize readability over aesthetics.
- Overly Loose Spacing: Using interline spacing that is too loose can make the text feel disjointed and fragmented. Find a balance that provides sufficient space without sacrificing visual cohesion.
The Future of Interline Spacing
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the ways in which we interact with text. Future advancements in typography and design may lead to new and innovative approaches to interline spacing. For example, artificial intelligence could be used to automatically optimize interline spacing based on the content and context of the text. Additionally, new display technologies may allow for more precise control over interline spacing and other typographic parameters.
Conclusion
Interline spacing is a fundamental aspect of typography and design that plays a crucial role in readability, comprehension, and visual appeal. By understanding the principles of interline spacing and following best practices, you can create text that is both visually engaging and easily accessible. Whether you’re designing a website, creating a document, or simply writing an email, take the time to consider the interline spacing and how it can impact the overall user experience. Mastering interline spacing is a key step in becoming a skilled and effective communicator. Don’t underestimate the power of properly spaced lines; it can make all the difference in how your message is received and understood. [See also: Understanding Typography in Web Design] and [See also: Best Practices for Readable Web Content]. Remember to always prioritize readability and accessibility when making decisions about interline spacing, and your audience will thank you for it. Experiment with different values and find what works best for your specific needs and preferences. With practice and attention to detail, you can master the art of interline spacing and create text that is both beautiful and functional.